Salesforce creates skinny tables to contain frequently used fields and to avoid joins, and it keeps the skinny tables in sync with their source tables when the source tables are modified. To enable skinny tables, contact Salesforce.com Customer Support.
For each object table, Salesforce maintains other, separate tables at the database level for standard and custom fields. This separation ordinarily necessitates a join when a query contains both kinds of fields. A skinny table contains both kinds of fields and does not include soft-deleted records.
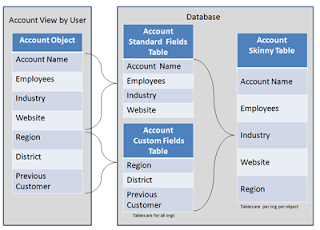
This table shows an Account view, a corresponding database table, and a skinny table that would speed up Account queries.
Need to contact Salesforce Customer Support or your Account Manager to enable skinny tables.
It can be created on custom objects, and on Account, Contact, Opportunity, Lead, and Case objects.
This table shows an Account view, a corresponding database table, and a skinny table that would speed up Account queries.
Skinny tables can contain the following types of fields.
- Checkbox
- Date
- Date and time
- Number
- Percent
- Phone picklist
- Picklist (multi-select)
- Text
- Text area
- Text area (long)
- URL
Skinny table can speed up queries. Instead of using a date range like 01/01/11 to 12/31/11—which entails an expensive, repeated computation to create an annual or year-to-date report—you can use a skinny table to include a Year field and to filter on Year = '2011'.
- Skinny tables can contain a maximum of 100 columns.
- Skinny tables cannot contain fields from other objects.
- Skinny tables are not copied to sandbox organizations. To have production skinny tables activated in a sandbox organization, contact salesforce.com Customer Support.
No comments:
Post a Comment